As marketers, we’re not strangers to rebranding and creating fancy new ways of saying things, but we have questions about ‘content decay’—like, for starters, where it came from (don’t worry, we’ll explain what it is later). Also, in this week’s Coffee & SEO, local search ads no longer use the location of the query being made as a ranking factor, video pages need to be about the video(s), you can now save custom filters in GA4, and OpenAI is bringing real-time results to ChatGPT.
Content Decay Trending as a New Term for Topic Depreciation
Don’t feel inept if you don’t know what ‘content decay’ is because not even Google’s Lizzie Sassman or John Mueller from Search Off the Record knew what it was. So what is it? Well, it’s a fancy new way of saying ‘old content that doesn’t rank anymore’ or topic depreciation.
For example, old blogs that are no longer generating traffic as a result of no longer being relevant or solving a problem that the content once did would be defined as suffering content decay.
Ways to Remediate Old Content That Has Lost Traffic
Before proceeding with remediation efforts, verify the data in Google Search Console or Google Analytics to confirm that the content is not generating traffic. You also want to check the content and see if it is still helpful and relevant. Because content is ‘old,’ it does not necessarily imply that it is no longer worth keeping.
If the content is no longer relevant or helpful, you have options available for remediating it:
- Update Content – Sometimes, content can be updated by updating statistics, data, or insights to current numbers or changing a few paragraphs to adjust relevance. When this is done, simply add a comment at the top of the page stating that the content was updated on ‘x’ date. This may be an optimal choice for content that is still generating low volumes of traffic and does not require a full rewrite to update the content.
- Rewrite the Content – If the topic of the content is still relevant but too outdated to save, you can rewrite it, focusing on what would create a helpful resource for your target audience. Research the keywords and phrases used for relevancy and intent.
When to Use a Redirect or Rel=Canonical Link
If you choose to rewrite the content or have content that is related to the topic, you can redirect or use rel=canonical to appropriately direct users and search bots to the URLs, but you want to be careful how rel=canonical is used. It could be considered bad practice.
Here are tips on when to implement redirects and when to use rel=canonical:
- Rel=Canonical – A rel=canonical link can be placed on content that is exactly the same topic or content on your website that has been rewritten or updated as a new URL. This identifies content as duplicate content, telling search engines that the same content can be found here and that you want them to index that page instead of the other URL.
- Redirect Content – When removing content from your website, a redirect should be used to negate 404 results when users or search bots attempt to access the deleted URL.
For example, if you have two URLs for the same content:
- Page 1 – http://example.com/page1.html
- Page 2 – http://example.com/page2.html
To indicate that http://example.com/page1.html is the version you want indexed and should be considered as the canonical URL, you would add the following tag to the <head> section of http://example.com/page2.html:
- <link rel=”canonical” href=”http://example.com/page1.html” />
This tells search engines that even though there are multiple URLs with similar content, http://example.com/page1.html is the authoritative version, consolidating the ranking signals for the preferred URL (more traffic to a single URL instead of sharing it).
Note that using a rel=canonical link instead of a redirect link to content that is not considered ‘duplicate’ or same topic content is considered ‘sneaky’ practice by Google and could negatively impact your website.
Location of Searcher Not a Ranking Factor for Local Ads
Where the person performing a search is located is no longer a ranking factor for local ads. Instead, Google considers what the user is searching for and your business’s relevancy in matching their query.
For example, if you own a restaurant and offer delivery services in a designated area, your business would only show up for searches within the areas you’ve identified.
However, if you offer custom t-shirts and have selected that your business is a national provider, shipping anywhere in the U.S., then Google would no longer restrict the search results your business populates for (i.e., local businesses to the person searching).
Optimize Your Google My Business Profile
A well-optimized Google My Business ( GMB) profile for your business is critical for your local ads populating search queries. You specifically want to pay attention to:
- Service or Job – Describe your service or work. Be clear and exact when describing this to help boost relevancy around your business and search query matches.
- Time of Search – Your hours of operation impact when your ads are displayed in search results. If your business is open 8am to 5pm CST, Monday through Friday, do not list your hours as 24/7. Missed calls and delayed response times could result in negative reviews, impacting your search ranking.
- Location of Search – Although the location of the person performing the query is no longer a ranking factor, the location of your business and the service area you identify is. For example, if you identify your service area as a 50-mile radius from location ‘x,’ your local ads will populate for queries that qualify within that area.
Watercooler Highlights
You can now save filter customizations in GA4, saving you time, money (and sanity). Plus, Google reiterates that in order to be considered video content, your content has to be, um, well, video content.
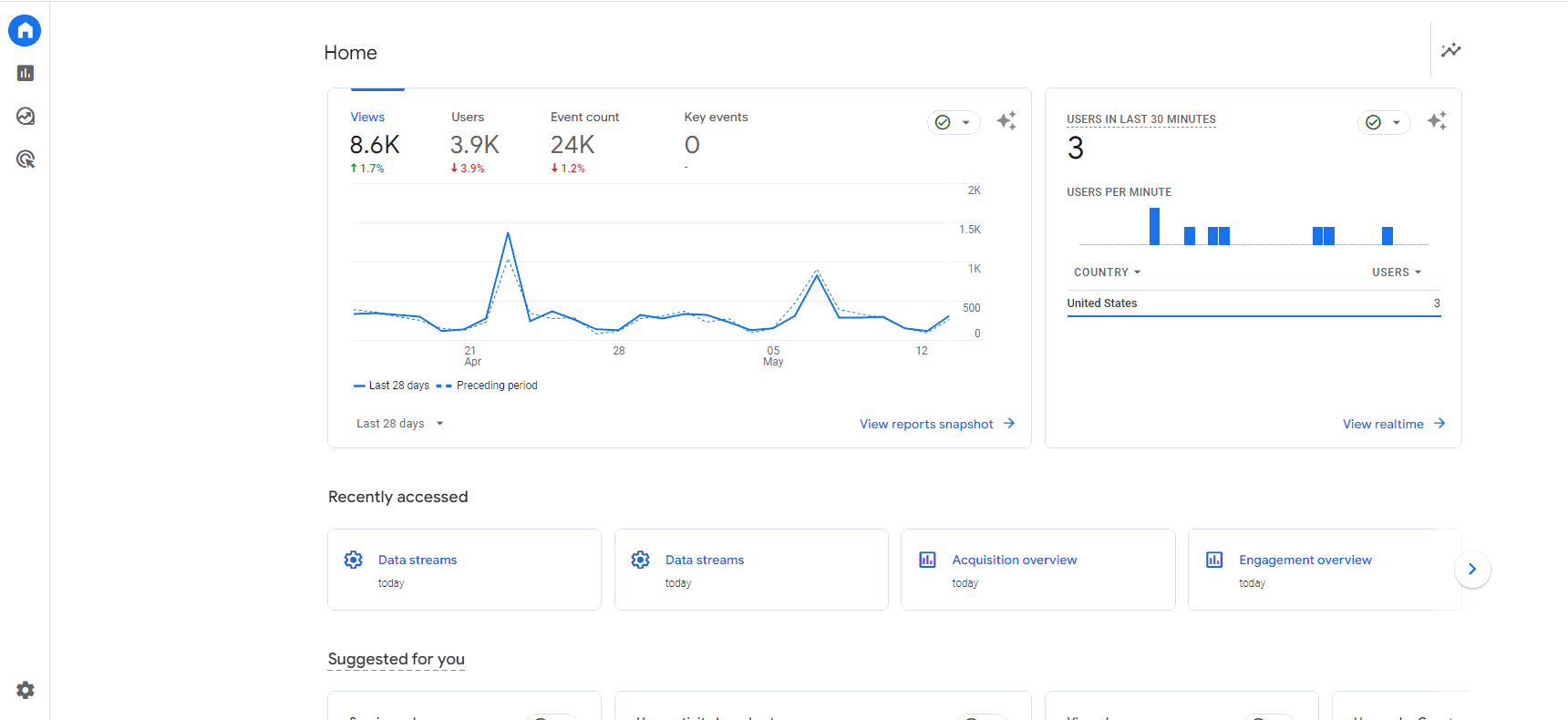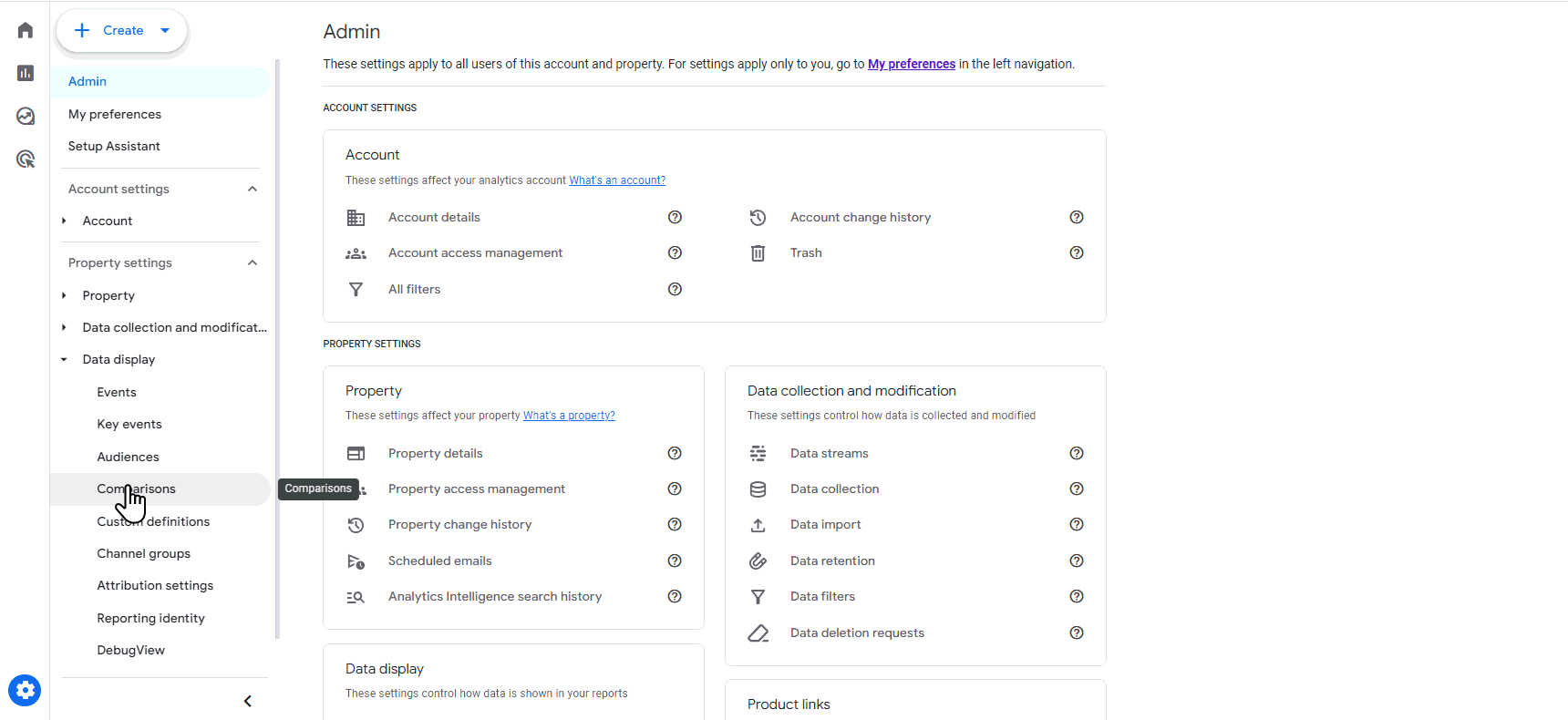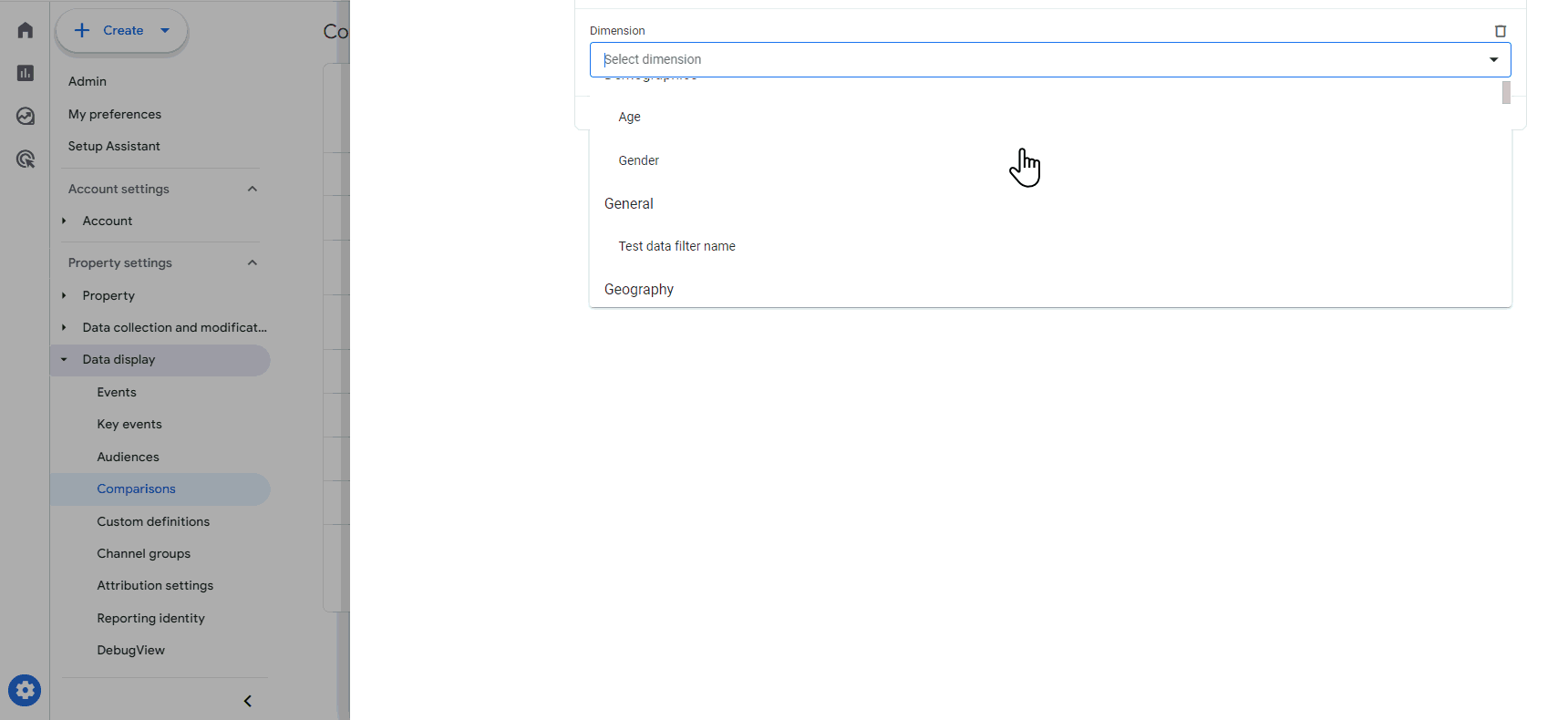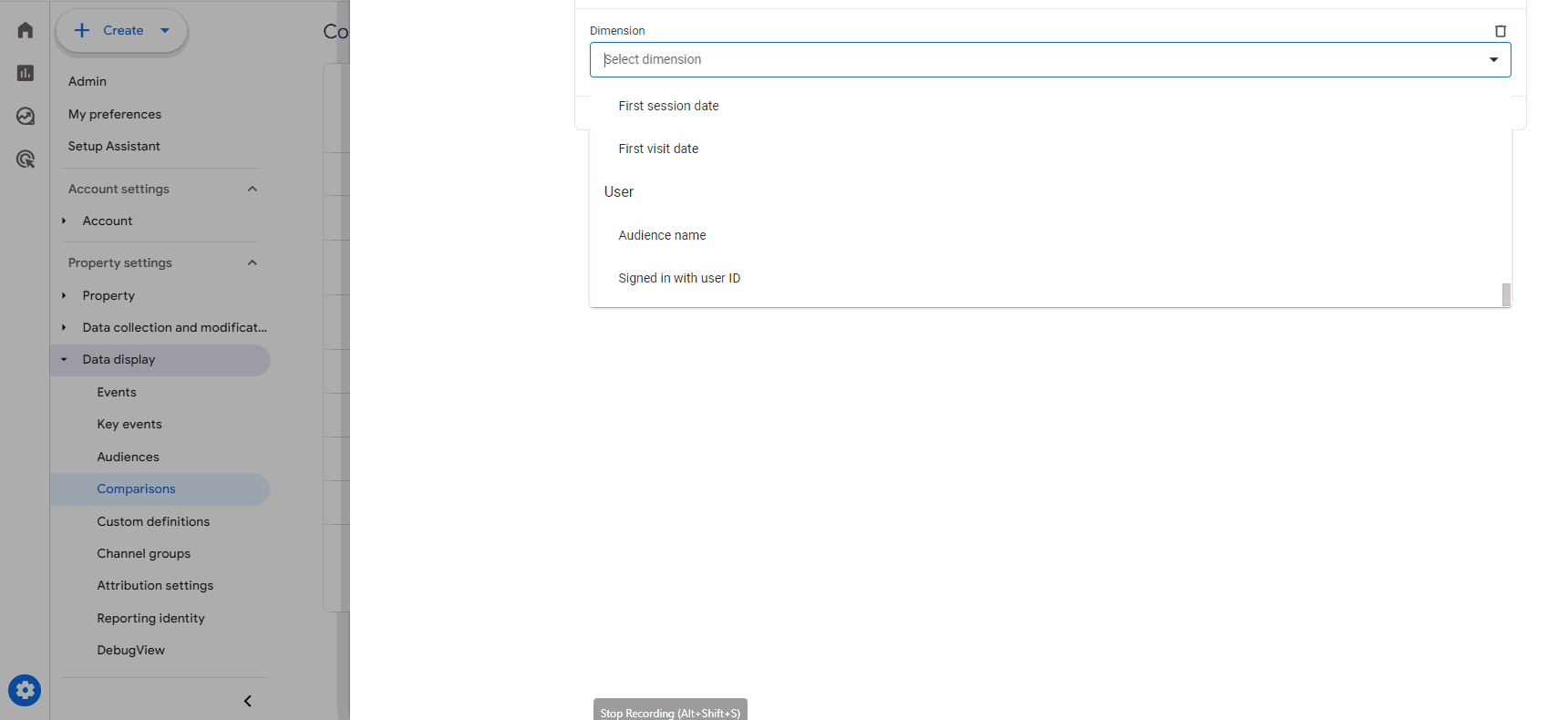
Save Filter Customization in Google Analytics 4
Google is rolling out a new feature in Google Analytics 4 (GA4) that allows you to save customized filters. If you don’t have this feature yet, give it time; it is still being rolled out.
But, in the meantime, here is how to access this time-saving new feature:
- Once logged in to your GA4 account, click on admin.
- From the admin panel, you’re going to want to click on data display.
- In the data display sub-menu, you will want to select comparisons.
- Click the new comparison button to the right of the search bar, just below quota information.
Video Pages Need to Be Video Pages, Not Content Pages
If you have more than a few sentences of content on a webpage with a video, that content is not going to rank or be indexed as a video page. And, if you want to compete with YouTube, TikTok, and other video platforms, then you want to make sure your video content is indexed and ranking how you’re wanting it to. Google has been clear about what constitutes ‘video content’ and what doesn’t. However, there were still some questions, and Google’s John Mueller replied, reiterating that video content pages need to be very obvious.
In other words, the webpage centerpiece annotation, or focal point, must be the video.
Creating Video Content Pages
The video should be the main focus of the webpage. This means that if there is written content, it is sparse and practically nonexistent. A couple of sentences, that’s it. The main focus and source of information should be from the video content.
“The “prominence” of a video on the page is an important signal to Google about whether or not the video is considered to be the main content of the page. In a page with multiple videos, a prominent video will typically be chosen ahead of a non-prominent video for indexing.” – Search Console Help, Video Indexing Report
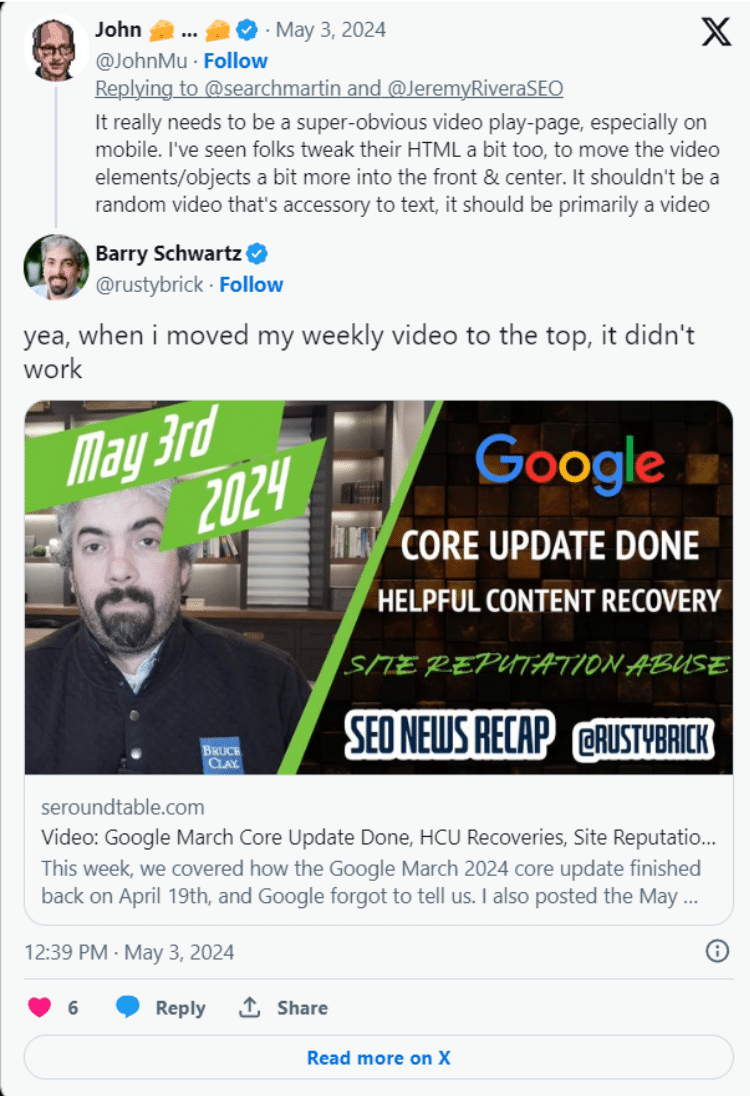
As Barry Schwartz from Search Engine Roundtable noted, moving your video to the top of the webpage with written content below it still does not qualify the webpage as video content. Search engines will still view the video as an accessory or amplifier of the written content.
Video Pages and Transcripts
Transcription for the video should be provided as a link below the video and a caption throughout the video itself. We can see an example of best practices on the Google Search Off the Record webpage.
Explore Latest Posts
From Feast-or-Famine to Predictable Revenue: Creating Consistency in Lead Generation The revenue roller coaster is exhausting. Some months your pipeline ... read more
February 25, 2026
Marketing Automation Tools That Actually Save Time (Not Create More Work) Your marketing to-do list keeps growing faster than you ... read more
February 18, 2026
The Hidden Costs of Managing Your Own Google Ads: What Most Business Owners Miss Google Ads seems straightforward enough: pick ... read more
February 11, 2026
Essential Strategies for Entrepreneurs
Get Actionable Business Insights & Marketing Tips
Our newsletter delivers real-world strategies from entrepreneurs who’ve been exactly where you are.
Sign up now for:
- Actionable growth strategies that work
- Insider tactics for attracting top talent
- Real-world case studies from successful founders
- Emerging tech trends that drive innovation
- Pragmatic marketing approaches for visionary leaders