In 2011, Google first changed how content was written with the Panda Update by changing how keywords could be used to make content rank. This was the first push for content to help the buyer in their search efforts, penalizing websites that were stuffing the same related terms 100 times in a 600-word article in an attempt to rank in the search results.
Since then, Google has been rolling out updates to tighten loose ends, deindexing websites that provide spammy content and lack a purpose-driven, user-centric focus.
The Evolution of Google’s Algorithm Updates
Initially, Google’s algorithms favored keywords, leading to black-hat SEO practices like keyword stuffing. Overloading content with keywords to manipulate rankings prioritized search visibility over providing value to the user, diminishing the quality and readability of the content.
In an attempt to offset this, Google continued to roll out content-directed updates, starting with:
- The Panda Update (2011) – Google’s Panda update was a game-changer. It targeted sites with low-quality content, excessive keyword stuffing, and a poor user experience. This update highlighted the need for well-written, informative content and penalized websites that failed to meet these criteria.
- The Penguin Update (2012) – Following Panda, the Penguin Update further refined the focus on quality content by penalizing sites engaged in manipulative link schemes and keyword stuffing. This update reinforced the importance of building a natural link profile and creating content that genuinely serves the user’s interests.
- Hummingbird and Beyond (2013) – The introduction of the Hummingbird update marked a significant shift towards natural language processing and understanding user intent. This update allowed Google to handle conversational queries better by emphasizing contextual matching of search queries with relevant content.
The Beginning of the Helpful Content Update
With all the updates and comments from Google about ‘user-centric content,’ everyone started producing content that focused on the buyer, and we can stop here, right? Not a chance. Marketers ruin everything, remember?
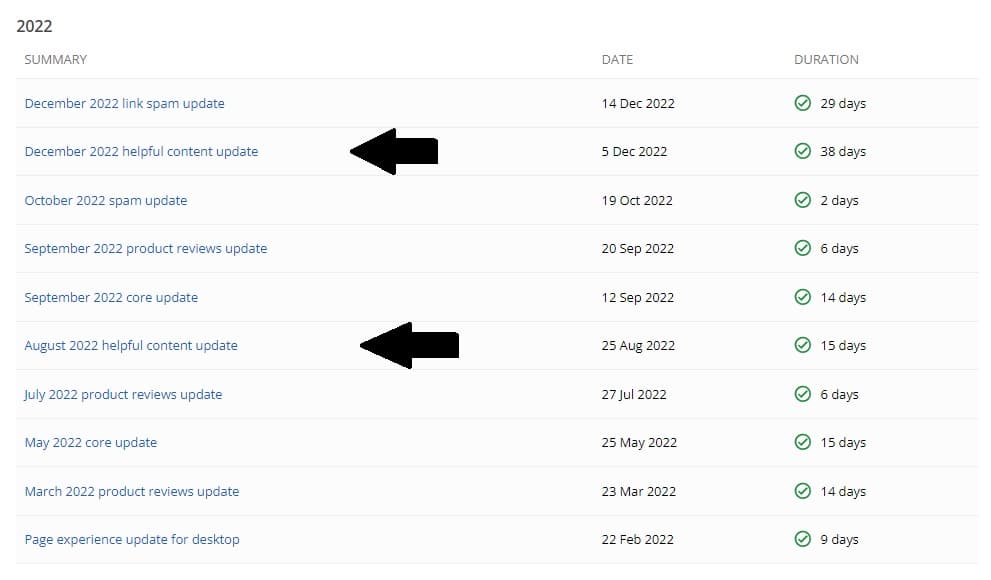
On August 18, 2022, Google first introduced the Helpful Content System & Ranking update. This update targeted low-quality content written primarily to rank well on search pages rather than provide value to the reader. The initial rollout of this update began on August 25, 2022, and was completed 15 days later on September 9, 2022.
This was the start of a series of updates meant to improve the quality of content in search results by prioritizing the user, not the search engines.
Google continued to refine and expand its algorithm with another rollout in December 2022 as well as the fateful September 2023 Helpful Content update, which had a noticeable impact on the SEO industry.
Source: Google Search Status Dashboard, 2022 Overview
Affecting many sites, with some never recovering due to a direct lack of user-centric content, this was the first aggressive update seen that directly targeted content that was not helpful. The update directly sought out poor content quality and relevance, looking for original, unique content written to have a helpful conversation with the user, not to play into the algorithm.
Google Spam Update of March 2024
The Google Spam and Core updates of March 2024 continued the helpful content efforts by introducing new policies, refining existing algorithms, and emphasizing the importance of high-quality, user-focused content.
The Spam update took about 15 days, targeting:
- Scaled content production
- Expired domains
- Authority abuse
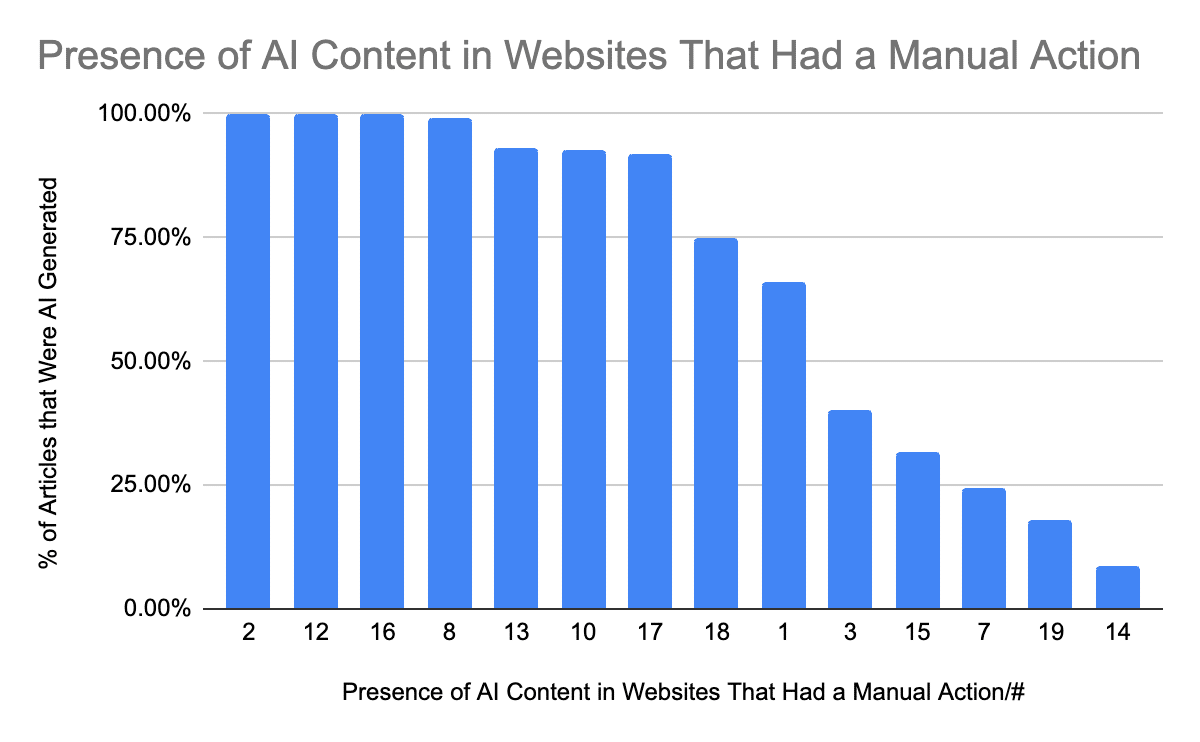
Immediately after the March 5th rollout, there were significant gains and losses across various domains, with some websites experiencing complete removal from Google’s search index. A study by Originality.ai found that 100% of the deindexed websites they studied showed signs of having 90% or more of their content generated by AI.
Source: Originality.ai, Can Google Detect and Does it Penalize AI Content
Additionally, this update saw both Manual Actions and Algorithmic Penalties. While Google Content Moderators issue manual actions and result in notifications via Search Console, algorithmic penalties do not come with a notice—you simply stop seeing organic traffic to your website.
Google March 2024 Core Update
The Core update incorporated Google’s helpful content system into its overall core ranking system, which means there are no more ‘Helpful Content Updates.’ They are all now ‘Google Core Updates.’
This recent update is still being rolled out and is more complex than previous core updates. It affects multiple core systems within Google’s algorithm and aims to reduce unhelpful, low-quality content in search results by 40%.
Due to the update’s complexity, more fluctuations in rankings are anticipated as different systems get fully updated. The update intent is to allow Google’s algorithms to understand which webpages are unhelpful or seem to be created, written, generated, etc., with search engine ranking as the top priority versus that of producing helpful, user-centric content with a purpose.
How a Content Audit Will Help You Avoid Penalties
Google has been committed to improving the quality of search results by targeting spammy practices and prioritizing helpful and high-quality content since 2011. The difference now is that Google is done playing nice. They have tightened their policies and are now taking strict action against those who violate them.
Complying With Google Guidelines With Quality Content
Auditing content to comply with Google’s guidelines and focus on creating original, valuable content for your buyers can no longer be pushed down your priority list. By removing or improving outdated, irrelevant, or low-quality content, you enhance the overall user experience and show Google you have your priorities straight.
Through manual evaluations of webpage content, just as Google does, there is attention to:
- The readability of the content.
- The tone and voice.
- The phrasing and language used.
- The connection between your content and the reader.
Google is not backing down and is very clear on what they expect. If you’re not sure if your content is helpful and up to par, reach out to Plan Left for a content audit today.
Explore Latest Posts
From Feast-or-Famine to Predictable Revenue: Creating Consistency in Lead Generation The revenue roller coaster is exhausting. Some months your pipeline ... read more
February 25, 2026
Marketing Automation Tools That Actually Save Time (Not Create More Work) Your marketing to-do list keeps growing faster than you ... read more
February 18, 2026
The Hidden Costs of Managing Your Own Google Ads: What Most Business Owners Miss Google Ads seems straightforward enough: pick ... read more
February 11, 2026
Essential Strategies for Entrepreneurs
Get Actionable Business Insights & Marketing Tips
Our newsletter delivers real-world strategies from entrepreneurs who’ve been exactly where you are.
Sign up now for:
- Actionable growth strategies that work
- Insider tactics for attracting top talent
- Real-world case studies from successful founders
- Emerging tech trends that drive innovation
- Pragmatic marketing approaches for visionary leaders