Google says the quality of your webpage is a ranking factor, but what is ‘quality’ according to Google? That would be the originality of your content. Additionally, Google’s CEO says AI has been integrated with Google search since 2016 and will only continue to improve search results for users. This means that SEO is, in fact, not ‘dead.’ Actually, SEO is more valuable now than ever with the integration of Generative Engine Optimization (GEO) for Generative (AI) Search.
Google CEO Says AI Improves Search, SEO Still Necessary
Google’s CEO Sundar Pichai does not see a future without SEO. AI has been integrated into how Google works since 2016, so the sudden concern about AI’s involvement in search is understandable but unnecessary.
As with anything else, we must evolve with the progression of technology—and SEO is constantly changing. Search algorithms are regularly updated, and it is necessary to stay current, or your business will get left behind.
AI Search v. AI ChatBots
As we have said in several other Coffee and SEO blogs, Generative Engine Optimization (GEO) is the future of search. However, to understand its value, we first need to clarify the difference between AI Search and AI ChatBots.
- AI Search – AI-based algorithms and natural language processing are used on platforms like Brave and Metaphor AI to supply accurate and relevant results to the user’s query.
- AI ChatBots – These are programs that are meant to imitate human conversation using AI and natural language processing, such as ChatGPT and Google Bard.
AI Search and GEO
With Search Generative Engine (SGE) still being tested in Google’s Search Lab, we can see how SGE is progressing and will impact search as we currently know it. We have covered a few studies that have been conducted on SGE in our Coffee and SEO blogs, and what has been consistent is that what works now for ranking terms and content will not work with SGE. This prompted the development of Generative Engine Optimization (GEO).
The most direct impact is on keyword use. Traditionally, with SEO, there is a review of terms, most often short-tail terms (one or two words) that you focus on within your web pages based on topic, product, or service. With GEO, the focus is on long-tail keywords and phrases that answer a query directly.
Query example: What playground equipment does the playground have?
- SEO – Swings; Slide; Soccer Field; Basketball Hoop
- GEO – Playground equipment options are swings, a slide, two basketball hoops, and a soccer field.
Creating sentence structure and phrases for GEO can and does happen organically, but the key is that GEO is not a singular focus. GEO is a holistic approach to make sure the user is getting the most accurate results available. If you are not already integrating this and other GEO strategies into your processes, now is the time to make those mergers.
How Google Understands Queries and Content Is Ranked
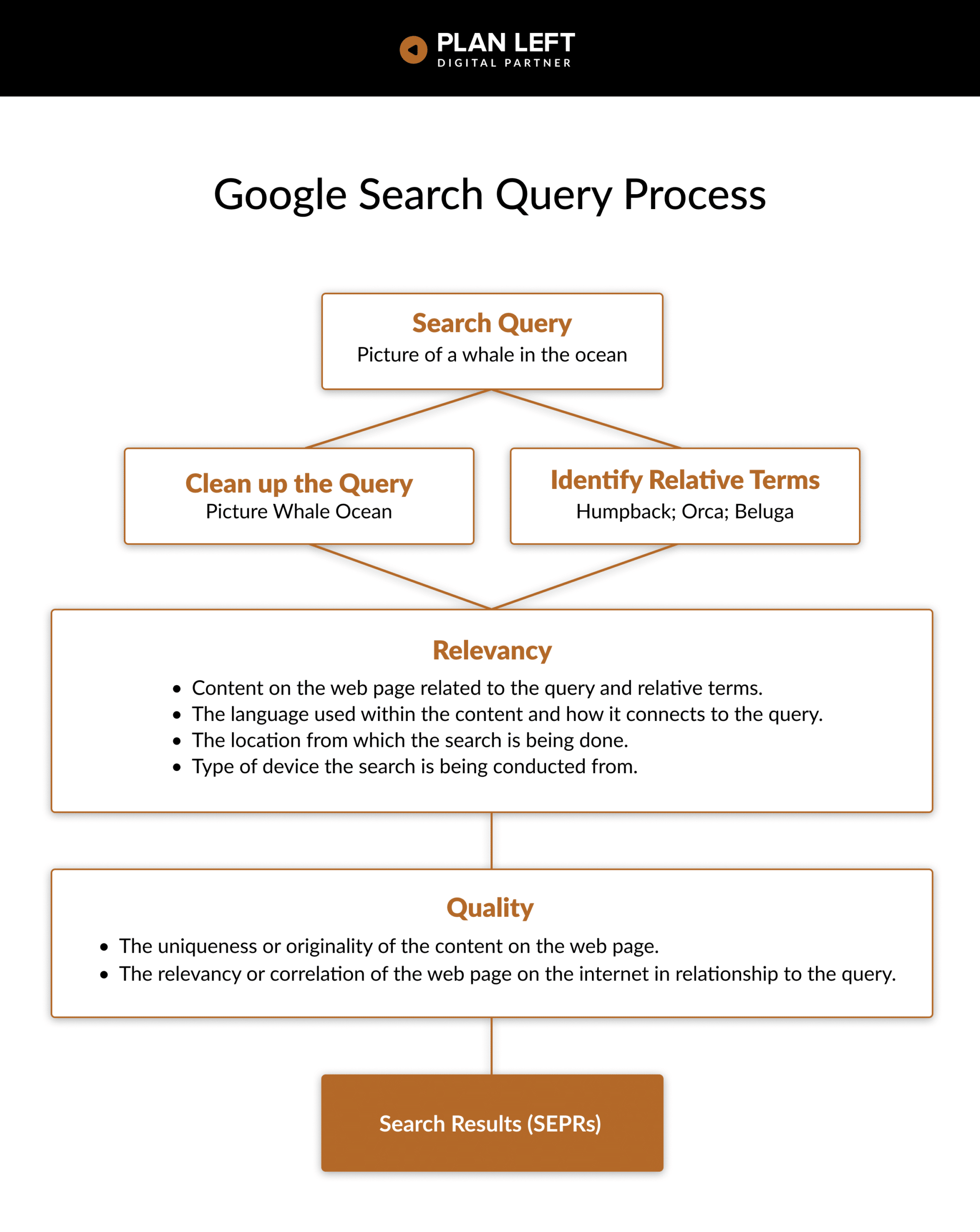
Google’s Garry Illyes breaks down how Google Search works in his latest video, “How Google Search Serves Pages.” Contrary to what you may think, Google does more than connect words used in a search query to words on a content page.
Start By Breaking Down the Query
As soon as you, the user, hit enter on the query, Google’s system gets busy on your search by first removing the filler terms or words that aren’t necessary for the search. For example, “Picture of a whale in the ocean” does not require ‘of,’ ‘a,’ or ‘the.’
So, with the ‘clean’ query of “Picture Whale in Ocean,” Google connects relative terms for the main focus of the search: Whale. Relative terms would be anything from Humpback to Orca or Beluga whales.
From Query to Ranking Content
With the query and relative terms, Google now looks at the indexed web pages across the internet, looking at relevance and quality to determine rank:
Relevance
- Content on the webpage related to the query and relative terms.
- The language used within the content and how it connects to the query.
- The location from which the search is being done.
- Type of device the search is being conducted from.
Quality
- The uniqueness or originality of the content on the web page.
- The relevancy or correlation of the web page on the internet in relationship to the query.
Remember that Google also places significant weight on the helpfulness of content, with the goal always being to place the most useful and relevant search results in front of the user. To stay relevant and make sure your content is top-quality, perform regular content audits.
Google Confirms Crawl Budget Assigned to Hostname
Your crawl budget is how many pages Google has permitted to be crawled for indexing on your website, and no, this number is not fixed and can change from day to day. You can see what your website’s crawl budget is by logging into Google Search Console and following the process:
- Google Search Console
- Select your website (if more than one is an option)
- Settings
- Under ‘Crawling’ you will see ‘Crawl Stats’

So, the question that came up was, how is the crawl budget allocated between different domains and subdomains?
Google’s John Mueller and Gary Illyes confirmed that each hostname has a different crawl budget. This means that each domain and subdomain has its own crawl budget—it’s not shared amongst them all. This is great news if you have hundreds or thousands of web pages per hostname and are worried about all of your product pages, older blogs, articles, etc., getting displaced while making room for newer content or more products.
Watercooler Highlights
Core Web Vitals focuses a lot, okay, mostly, on speed. Everyone wants what they want instantaneously, especially when it comes to searching the internet. WordPress heard the call, and their new plugin does not disappoint. Also, California’s bill in legislation looks to tax Google and social media news links.
Speculative Loading API Plugin From WordPress Offers Almost Instant Load Times
User conversions are directly affected by page load speeds, with a 1.9% conversion rate for load speeds averaging 2.4 seconds and less than 1% for anything higher than 4 seconds. WordPress heard the callout for a single plugin that would offer that instant load time, and they delivered.
WordPress Performance Plugin improves website loading times by optimizing various elements such as:
- Faster Loading Times – By implementing lazy loading for images, CSS, and JavaScript files, the plugin makes sure that only the essential content is loaded initially, speeding up the page load time.
- Resource Delivery – Through advanced caching techniques, the plugin stores frequently accessed resources like images and files in a cache, reducing the time it takes to retrieve them from the server and improving overall page loading speed.
- Proactive Resource Preloading – The Speculative Loading API predicts which resources visitors might need next based on their browsing behavior and preloads them in the background. This proactive approach minimizes delays in accessing content, further speeding up the browsing experience.
Faster loading times directly impact search engine rankings, with search engines like Google prioritizing websites that provide a better user experience and, as we mentioned earlier, improve conversion rates. This plugin could be the game-changer you’ve been looking for.
Google Starts Cutting California Out of Local News Ahead of Bill in California Legislature
The California Journalism Preservation Act is gaining a lot of attention. The proposed bill would make search and social platforms like Google and Meta pay for links to news articles.
Source: California Legislative Information, AB-886 California Journalism Preservation Act
If this law passes, Google says they might stop showing news links in California. Google has begun pulling news links in some areas of California to test the impact of pulling them all together. When we investigated this, we did not see any reduction in news links… yet.
Something similar happened before with Spain, but ultimately, Spain decided to forego the law that was enacted, Google News came back, and all has been well since.
The intent of the bill is to protect journalism, but at the same time, there is no way for journalists to opt out of the California Journalism Preservation Act. So, to be continued…
Laws are changing, and Google is deindexing websites more than ever. Don’t leave it to chance. Contact us and know it’s done right.
Explore Latest Posts
Google says the quality of your webpage is a ranking factor, but what is ‘quality’ according to Google? That would ... read more
April 19, 2024
In 2011, Google first changed how content was written with the Panda Update by changing how keywords could be used ... read more
April 17, 2024
The latest Google algorithm changes have shaken the search marketing world. While the Google Spam update has finished, the Google ... read more
April 16, 2024
MARKETING insights
Join the Thousands Who Receive Our Twice-Monthly Newsletter.
It's hard to keep up. Our newsletter is packed with buyer behavior insights, the latest marketing and technology updates, work/life balance tips, and—because we ❤️ our support staff—adorable pets looking for forever homes. Only twice per month. No clogged inboxes. You can't say no.